


Google’s retention policy describes how and why Google retains data. Although this policy describes features that are specific to Chrome, any personal information that is provided to Google or stored in your Google Account will be used and protected in accordance with the Google Privacy Policy, as changed from time to time. Most web developers use the query string approach and use a version suffix to send the new file to the browser.Learn how to control the information that's collected, stored, and shared when you use the Google Chrome browser on your computer or mobile device, Chrome OS, and when you enable Safe Browsing in Chrome. There’s no way to do that effectively across all browsers and proxies from the webserver by manipulating cache headers unless you change the file name or you change the URL of the files by introducing some unique query string so that browsers/proxies interpret them as new files. You need some way to force browser and proxy(s) to download latest files. When you update javascript or css files that are already cached in users’ browsers, most likely many users won’t get that for some time because of the caching at the browser or intermediate proxy(s). Automatic Javascript, CSS versioning to refresh browser cache : You could add many types of characters to the query string value, but numbers are a logical way to do it, because then you can just increase the number, and even add decimal places if you want.Īnd of course, if you don’t change the value for a while, the browser will continue to cache (or preserve) the file, and won’t attempt to download it unless other factors force it to, or you end up updating the query string value.

It will only serve to make the browser think it’s a completely different file.
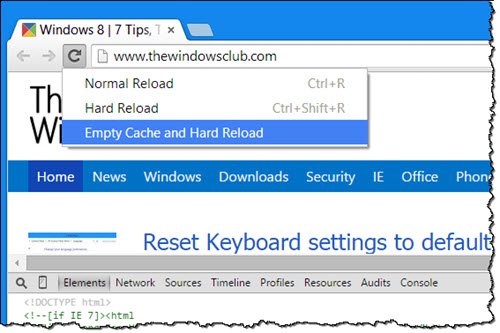
If you’re new to query strings, just know that the part before the equals sign is like a placeholder, and the part after the equals sign is the value put into that placeholder. So, each time you update your CSS on the server, you can incrementally update your version number. The browser will view a file name of style.css as different from a file name of style.css?v=1.1, so it will generally force the browser to update the stylesheet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
